
Balance sheets, like all financial statements, will have minor differences between organizations and industries. However, there are several “buckets” and line items that are almost always included in common balance sheets. We briefly go through commonly found line items under Current Assets, Long-Term Assets, Current Liabilities, Long-Term Liabilities, and Equity. Understanding the difference between normal balance retained earnings and revenue is crucial for financial literacy and decision-making. While both are essential for business operations, they have distinct roles and sources.
Are Companies Making Fewer Errors in Financial Reporting?
- Retained Earnings represents the portion of cumulative net income kept within the business structure.
- Buybacks are recorded as cash outflows in the financing section of the statement of cash flows.
- This offset is supported by a material projected ECR-related deposit cost decline this year and an increase in mortgage banking revenue in this scenario based upon our rate cut forecast.
- Many states restrict retained earnings by the cost of treasury stock, which prevents the legal capital of the stock from dropping below zero.
- Thus, the balance in Retained Earnings represents the corporation’s accumulated net income not distributed to stockholders.
The cash flow statement shows cash movements from operating, investing, and financing activities. A classified balance sheet is a financial statement in which assets, liabilities, and equity are categorized into specific groups based on their expected recovery or settlement periods. This format groups accounts into sections such as current assets, long-term assets, current liabilities, and long-term liabilities, making the information easier for readers to understand and analyze. The understanding of this structure is essential for organizations that need to prepare a classified balance sheet that clearly presents a company’s resources and obligations at a specific point in time.
Par value method
Businesses operate in one of three forms—sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations. Sole proprietorships utilize a single account in owners’ equity in which the owner’s investments and net income of the company are accumulated and distributions to the owner are withdrawn. Corporations differ from sole proprietorships and partnerships in that their operations are more complex, often due to size. Unlike these other entity forms, owners of a corporation usually change https://raizesdamata.com.br/small-business-bookkeeping-services-in-dallas/ continuously.
- His contributions to the company are too numerous to list, but his skill and leadership were particularly evident during my absence at the beginning of the year.
- In the short run, the other benefits to moving the LFI threshold of $250 billion would be to free up technology resources to support our product line and service improvement development.
- As a result, it supports deeper financial analysis, particularly in evaluating liquidity, solvency, and the company’s ability to meet financial obligations.
- When treasury shares are retired, the shares are permanently cancelled and no longer considered issued.
- For example, a state corporate code may prohibit dividends if they would cause net assets to fall below stated capital.
Add Up Totals for Each Category

Occasionally, accountants make other entries to the Retained Earnings account. The retained earnings portion of stockholders’ equity typically results from accumulated earnings, reduced by net losses and dividends. Like paid-in capital, retained earnings is a source of assets received by a corporation.
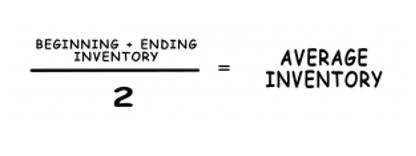
Current Assets
- The statement of changes in equity shows the movement in equity, including the treasury stock balance, APIC adjustments and any retained earnings impacts on reissuance or retirement.
- Noninterest expense increased $14 million or 3% quarter-over-quarter as deposit costs rose $10.6 million due to the normal seasonal rebuild in mortgage warehouse deposits, which pushed average balances higher.
- The purpose of retaining these earnings can be varied and includes buying new equipment and machines, spending on research and development, or other activities that could potentially generate growth for the company.
- The announced CFO succession and corporate brand consolidation signal ongoing investments in leadership and operational scalability as the company targets organic growth approaching the $100 billion balance sheet threshold.
- Readers will learn how small and large stock dividends are measured and recorded, how the statement of retained earnings is affected, and what investors and analysts should watch for.
This entry increases assets (cash) and increases equity accounts tied to contributed capital (common stock and APIC). Therefore, issuing stock for capital does not directly change retained earnings. The entry to correct the error contains a decrease to Retained Earnings on the statement of retained earnings for $1,000.
What is the purpose of a balance sheet?

Prior period adjustments are corrections of errors that appeared on previous periods’ financial statements. These errors can stem from mathematical errors, misinterpretation of GAAP, or a misunderstanding of facts at the time the financial statements were prepared. Many errors impact the retained earnings account whose balance is carried forward from the previous period. Since the financial statements have already been issued, they must be corrected. The correction involves changing the financial statement amounts to the amounts they would have been had no errors occurred, a process known as restatement.

Retained Earnings is fundamentally classified as a component of Shareholders’ Equity on a company’s balance sheet. Shareholders’ Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all liabilities. IFRS for SMEs has only about 300 pages of requirements, whereas regular IFRS is over 2,500 pages and U.S. This means entities using IFRS for SMEs don’t have to frequently adjust their accounting systems and reporting to new standards, whereas U.S. At the end of a given reporting period, any net income that is not paid out to shareholders is added to the business’s retained earnings.

Impact on Financial Statements
Analysts must scrutinize the proportion of earned capital versus contributed capital to assess the quality and sustainability of the equity base. The source of capital significantly impacts financial analysis, particularly when evaluating a company’s return on equity (ROE) or its leverage. Conversely, a Net Loss for the period will decrease the RE balance, potentially resulting in a negative figure known as a deficit. This deficit indicates that the cumulative losses or distributions have exceeded the cumulative profits of the company. Unlike temporary accounts that close to zero at the end of an accounting period, RE is a permanent account that rolls its ending balance forward. The ending balance of one fiscal year automatically becomes the beginning balance of the next fiscal year.
Stuck with a Question?
The key events that occurred during the year—including net income, stock issuances, and dividends—are listed vertically. The stockholders’ equity section of the company’s balance sheet displays only the ending balances of the accounts and does not provide the activity or changes during the period. It is often referred to as net worth or net retained earnings assets in the financial world and as stockholders’ equity or shareholders’ equity when discussing businesses operations of corporations. From a practical perspective, it represents everything a company owns (the company’s assets) minus all the company owes (its liabilities).
In other words, prior period adjustments are a way to go back and correct past financial statements that were misstated because of a reporting error. The statement of retained earnings is a subsection of the statement of stockholders’ equity. The format typically displays a separate column for each stockholders’ equity account, as shown for Clay Corporation in Figure 5.49.
